Protection of Hidden Volumes Against Damage
If you mount a VeraCrypt volume within which there is a
hidden volume, you may
read data stored on the (outer) volume without any risk. However, if you (or the operating system) need to
save data to the outer volume, there is a risk that the hidden volume will get damaged (overwritten). To prevent this, you should protect the hidden volume in a way described in this section.
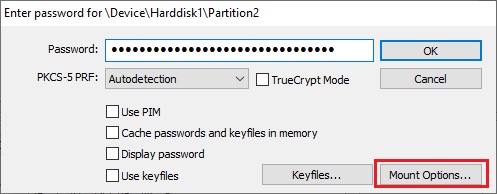
When mounting an outer volume, type in its password and before clicking
OK, click Mount Options:
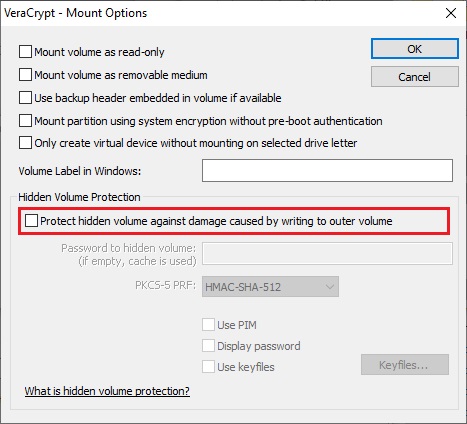
In the Mount Options dialog window, enable the option 'Protect hidden volume against damage caused by writing to outer volume '. In the 'Password to hidden volume'
input field, type the password for the hidden volume. Click
OK and, in the main password entry dialog, click
OK.
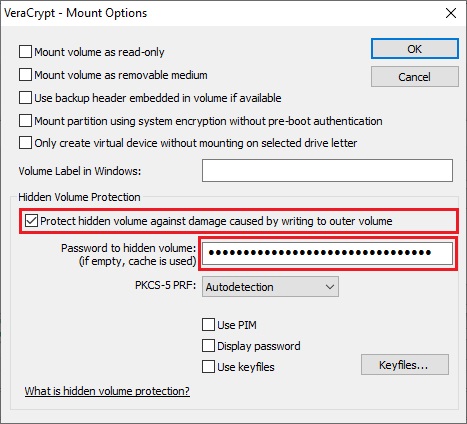
Both passwords must be correct; otherwise, the outer volume will not be mounted. When hidden volume protection is enabled, VeraCrypt does
not actually mount the hidden volume. It only decrypts its header (in RAM) and retrieves information about the size of the hidden volume (from the decrypted header). Then, the outer volume is mounted and any attempt to save
data to the area of the hidden volume will be rejected (until the outer volume is dismounted).
Note that VeraCrypt never modifies the filesystem (e.g., information about allocated clusters, amount of free space, etc.) within the outer volume in any way. As soon as the volume is dismounted, the protection is lost. When
the volume is mounted again, it is not possible to determine whether the volume has used hidden volume protection or not. The hidden volume protection can be activated only by users who supply the correct password (and/or keyfiles) for the hidden volume (each
time they mount the outer volume).
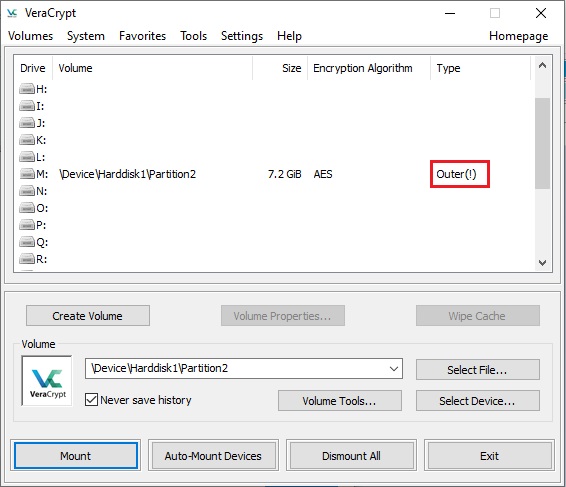
As soon as a write operation to the hidden volume area is denied/prevented (to protect the hidden volume), the entire host volume (both the outer and the hidden volume) becomes write-protected until dismounted (the VeraCrypt driver reports the 'invalid parameter'
error to the system upon each attempt to write data to the volume). This preserves plausible deniability (otherwise certain kinds of inconsistency within the file system could indicate that this volume has used hidden volume protection). When damage to hidden
volume is prevented, a warning is displayed (provided that the VeraCrypt Background Task is enabled – see the chapter
VeraCrypt Background Task). Furthermore, the type of the mounted outer volume displayed in the main window changes to '
Outer(!) ':
Moreover, the field Hidden Volume Protected in the
Volume Properties dialog window says:
'Yes (damage prevented!)'.
Note that when damage to hidden volume is prevented,
no information about the event is written to the volume. When the outer volume is dismounted and mounted again, the volume properties will
not display the string "damage prevented".
There are several ways to check that a hidden volume is being protected against damage:
-
A confirmation message box saying that hidden volume is being protected is displayed after the outer volume is mounted (if it is not displayed, the hidden volume is not protected!).
-
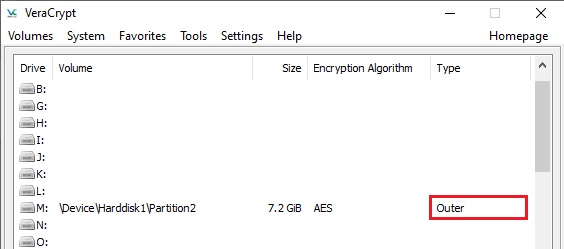
In the Volume Properties dialog, the field
Hidden Volume Protected says 'Yes':
-
The type of the mounted outer volume is Outer:
Important: You are the only person who can mount your outer volume with the hidden volume protection enabled (since nobody else knows your hidden volume password). When an adversary asks you to mount an outer volume, you of course
must not mount it with the hidden volume protection enabled. You must mount it as a normal volume (and then VeraCrypt will not show the volume
type "Outer" but "Normal"). The reason is that, during the time when an outer volume is mounted with the hidden volume protection enabled, the adversary
can find out that a hidden volume exists within the outer volume (he/she will be able to find it out until the volume is dismounted and possibly
even some time after the computer has been powered off - see
Unencrypted Data in RAM).
Warning: Note that the option '
Protect hidden volume against damage caused by writing to outer volume' in the
Mount Options dialog window is automatically disabled after a mount attempt is completed, no matter whether it is successful or not (all hidden volumes that are already being protected will, of course, continue to be protected).
Therefore, you need to check that option
each time you attempt to mount the outer volume (if you wish the hidden volume to be protected):
If you want to mount an outer volume and protect a hidden volume within using cached passwords, then follow these steps: Hold down the
Control (Ctrl) key when clicking
Mount (or select Mount with Options
from the Volumes menu). This will open the
Mount Options dialog. Enable the option 'Protect hidden volume against damage caused by writing to outer volume' and leave the password box empty. Then click
OK.
If you need to mount an outer volume and you know that you will not need to save any data to it, then the most comfortable way of protecting the hidden volume against damage is mounting the outer volume as read-only (see the section
Mount Options).
Next Section >>